broad_peak¶
Broad Lorentzian type peak on top of a power law decay
Parameter |
Description |
Units |
Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
scale |
Scale factor or Volume fraction |
None |
1 |
background |
Source background |
cm-1 |
0.001 |
porod_scale |
Power law scale factor |
None |
1e-05 |
porod_exp |
Exponent of power law |
None |
3 |
lorentz_scale |
Scale factor for broad Lorentzian peak |
None |
10 |
lorentz_length |
Lorentzian screening length |
Å |
50 |
peak_pos |
Peak position in q |
Å-1 |
0.1 |
lorentz_exp |
Exponent of Lorentz function |
None |
2 |
The returned value is scaled to units of cm-1 sr-1, absolute scale.
Definition
This model calculates an empirical functional form for SAS data characterized by a broad scattering peak. Many SAS spectra are characterized by a broad peak even though they are from amorphous soft materials. For example, soft systems that show a SAS peak include copolymers, polyelectrolytes, multiphase systems, layered structures, etc.
The d-spacing corresponding to the broad peak is a characteristic distance between the scattering inhomogeneities (such as in lamellar, cylindrical, or spherical morphologies, or for bicontinuous structures).
The scattering intensity I(q) is calculated as
Here the peak position is related to the d-spacing as q0=2π/d0.
A is the Porod law scale factor, n the Porod exponent, C is the Lorentzian scale factor, m the exponent of q, ξ the screening length, and B the flat background.
For 2D data the scattering intensity is calculated in the same way as 1D, where the q vector is defined as
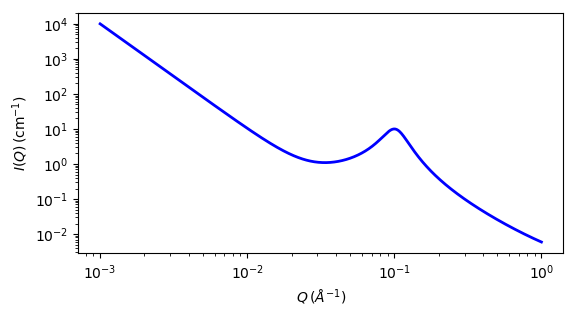
Fig. 99 1D plot corresponding to the default parameters of the model.¶
Source
References
None.
Authorship and Verification
Author: NIST IGOR/DANSE Date: pre 2010
Last Modified by: Paul kienle Date: July 24, 2016
Last Reviewed by: Richard Heenan Date: March 21, 2016