two_power_law¶
This model calculates an empirical functional form for SAS data characterized by two power laws.
Parameter |
Description |
Units |
Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
scale |
Scale factor or Volume fraction |
None |
1 |
background |
Source background |
cm-1 |
0.001 |
coefficent_1 |
coefficent A in low Q region |
None |
1 |
crossover |
crossover location |
Å-1 |
0.04 |
power_1 |
power law exponent at low Q |
None |
1 |
power_2 |
power law exponent at high Q |
None |
4 |
The returned value is scaled to units of cm-1 sr-1, absolute scale.
Definition
The scattering intensity I(q) is calculated as
where qc = the location of the crossover from one slope to the other, A = the scaling coefficient that sets the overall intensity of the lower Q power law region, m1 = power law exponent at low Q, and m2 = power law exponent at high Q. The scaling of the second power law region (coefficient C) is then automatically scaled to match the first by following formula:
Note
Be sure to enter the power law exponents as positive values!
For 2D data the scattering intensity is calculated in the same way as 1D, where the q vector is defined as
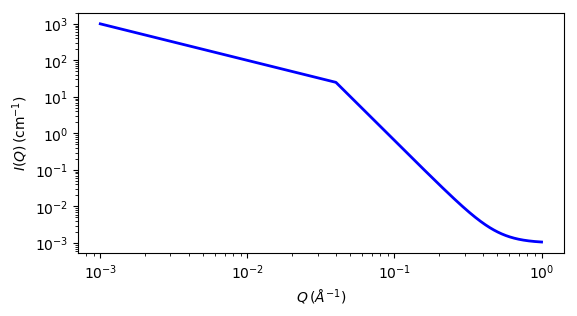
Fig. 125 1D plot corresponding to the default parameters of the model.¶
Source
References
None.
Authorship and Verification
Author: NIST IGOR/DANSE Date: pre 2010
Last Modified by: Wojciech Wpotrzebowski Date: February 18, 2016
Last Reviewed by: Paul Butler Date: March 21, 2016